The entire deployment flow¶
In this section we'll look into what really happened when we applied the configration to the kubernetes cluster.
When run the command kubectl apply, the file is taken and passed of to a Master that controls the kubernetes cluster, one of which is kube-apiserver which is responsible for monitoring the status of all the different nodes in the cluster and making sure that their are doing the correct things.
The kube-apiserver holds a table of it's state and updates it with the configuration passed.
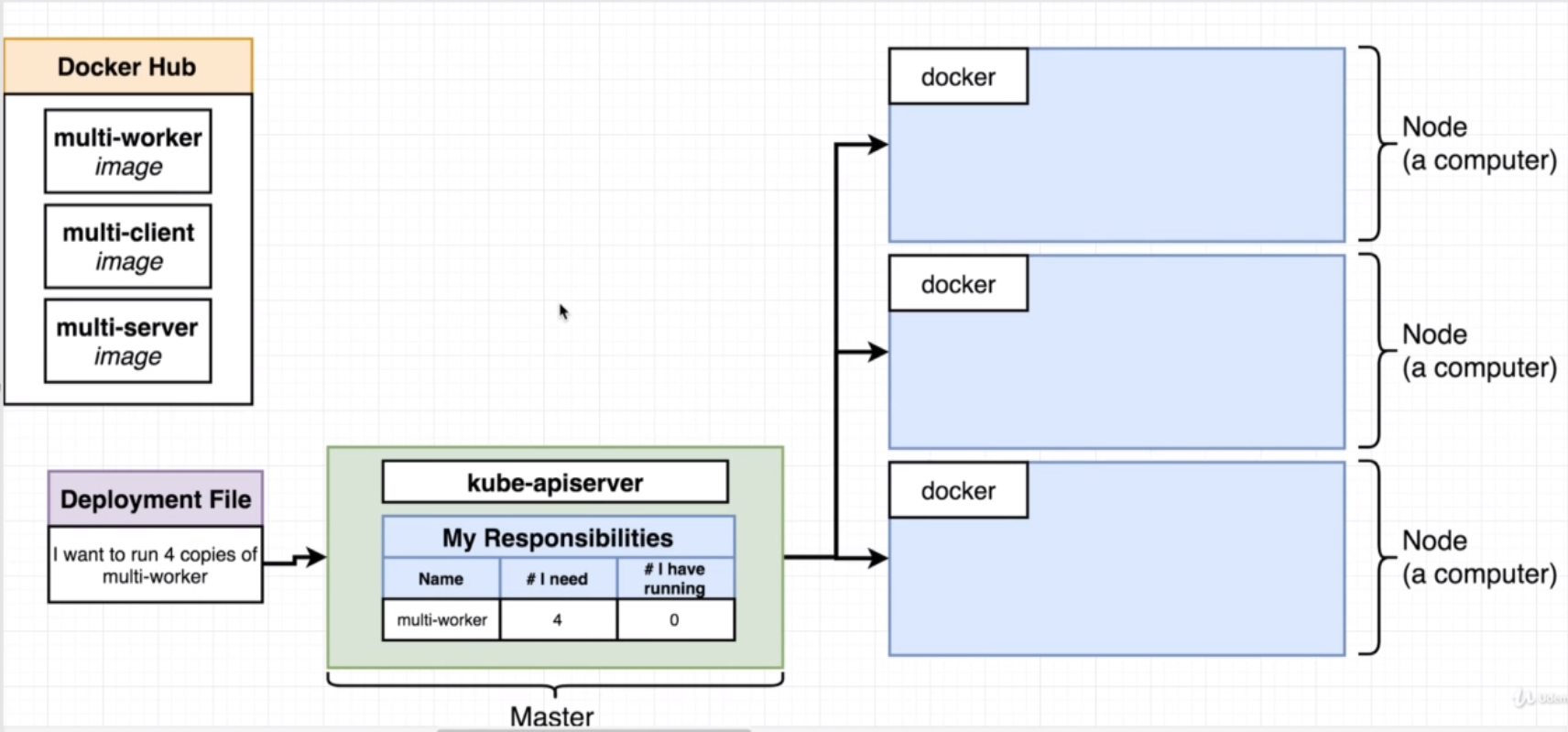
Then, based on it's state, it issues commands to nodes.
For example, if we tell the master that we want 4 copies of multi-worker, it will update it's state table and will see that it needs to be running 4 copies of multi-worker, but has 0. It will issue commands to nodes to start up those containers.
Then, the node will download the image from docker hub and start up the containers.
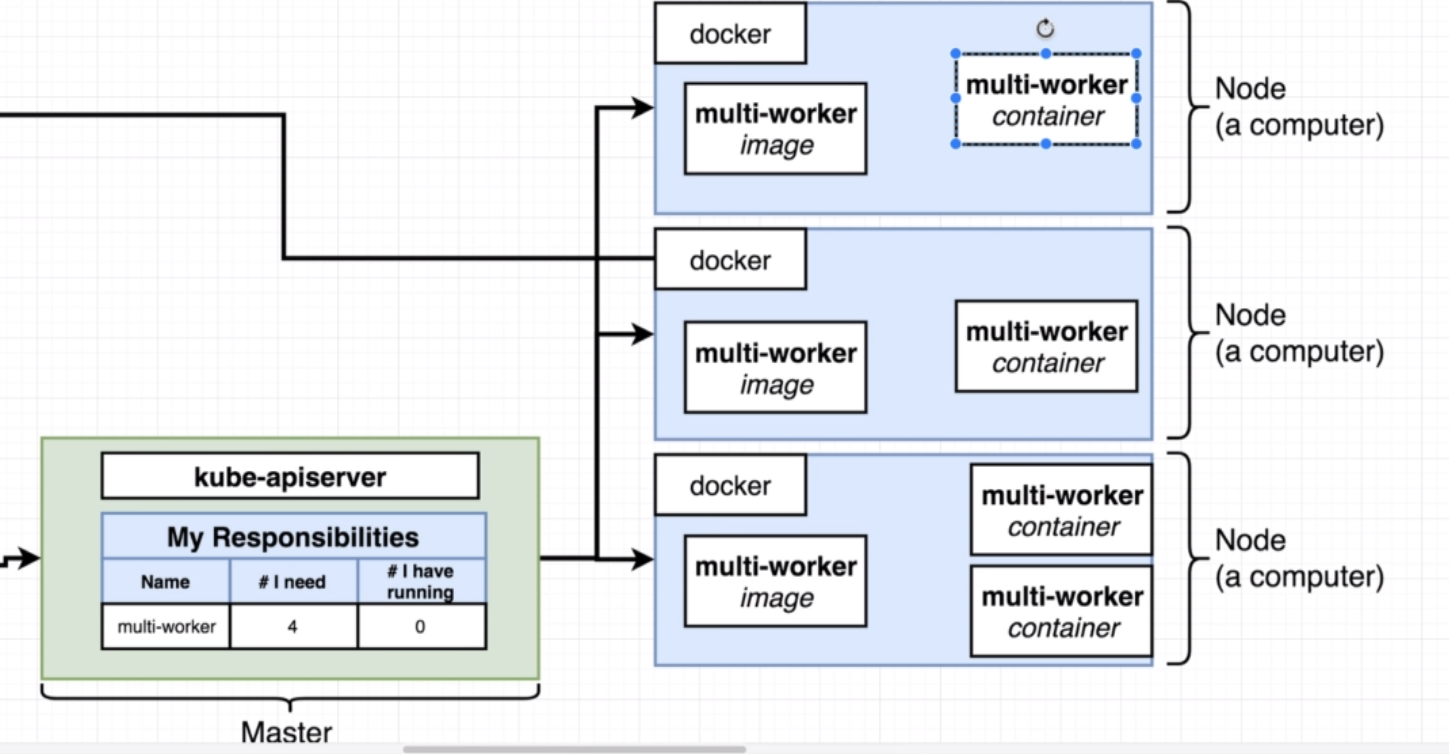
Then the Master will update poll the nodes and see that there are 4 containers of multi-worker running, update it's state table.
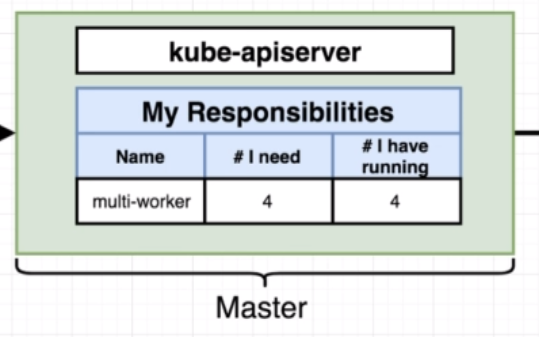
If for some reason one of these containers would be killed, the master would notice it and issue a command to the node to start it up again.