Binary heap operations¶
Implementation options¶
- Array based
- Reference / pointer based implementation
Array representation¶
At the logical level, the Binary Heap looks like this:
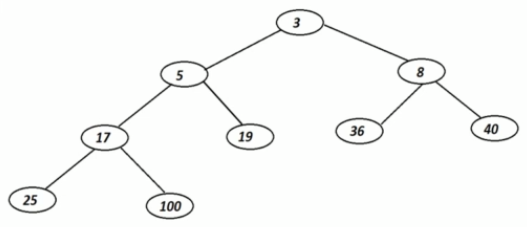
The binary heaps looks like this in the array implementation:

Left child - cell[2x]
Right child - cell[2x+1]
createHeap(size)
create a blank array of size+1
initialize sizeOfHeap with 0
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(n)
peekOfTop()
if tree does not exist
return error
return first cell of array
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
sizeOfHeap()
return sizeOfHeap // number of cells used in heap array
insertValueInHeap(value)
if tree does not exist
return error
else
insert value in first unused cell of array
sizeOfHeap++
heapifyBottomToTop(sizeOfHeap)
Time complexity - O(log n)
Space complexity - O(log n)
extractMin()
if tree does not exist
return error
extract 1st cell of array
promote last element to first
sizeOfHeap--
heapifyTopToBottom(1)
Time complexity - O(log n)
Space complexity - O(log n)
deleteHeap()
set array to null
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
Why avoid using reference based implementation?¶
When we extract from the heap, we delete the first note, get the last node and bring it to the top.
When using references, there is no way we can find out the last element of the tree in O(log n) time.