AVL implementation¶
createAVL()
root = null
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
searchAVL(root, value)
if( root is null )
return null
else if root == value
return root
else if value < root
searchAVL(root.left, value)
else if value > root
searchAVL(root.right, value)
Time complexity - O(log n)
Space complexity - O(log n)
preOrderTraversal(root)
if root == null
return error
print root
preOrderTraversal(root.left)
preOrderTraversal(root.right)
Time complexity - O(n)
Space complexity - O(n)
inOrderTraversal(root)
if root == null
return error
inOrderTraversal(root.left)
print root
inOrderTraversal(root.right)
Time complexity - O(n)
Space complexity - O(n)
postOrderTraversal(root)
if root == null
return error
postOrderTraversal(root.left)
postOrderTraversal(root.right)
print root
Time complexity - O(n)
Space complexity - O(n)
levelOrderTraversal(root)
create a queue
enqueue(root)
while(queue not empty)
dequeue and print
enqueue children
Time complexity - O(n)
Space complexity - O(n)
Now, the insertion and deletion operations are a little bit more complicated in case of AVL trees.
When we want to insert a node in AVL tree, there can be 2 cases:
1. When rotation is not required
2. When rotation is required (LL, LR, RR, RL)
We can determine whether we need rotation by checking if any nodes left tree and right tree height differs by more than 1 level.
When we want to do a rotation, there are there can be 4 conditions.
1. Left Left condition¶
Disbalanced node's grandchild is located on left, left subtree.
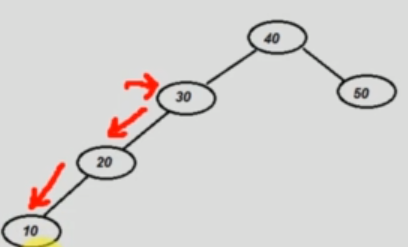
We do a right rotation:
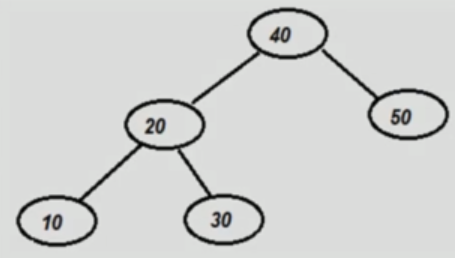
rightRotate(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot = currentDisbalancedNode.left
currentDisbalancedNode.left = currentDisbalancedNode.left.right
newRoot.right = currentDisbalancedNode
currentDisbalancedNode.height = calculateHeight(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot.height = calculateHeight(newRoot)
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
2. Left Right condition (LR)¶
Disbalanced node's grandchild is located in Left-Right position.
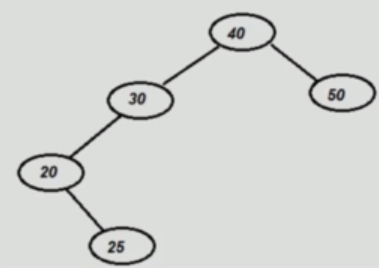
We do a left rotation, but on the disbalanced node's child position.
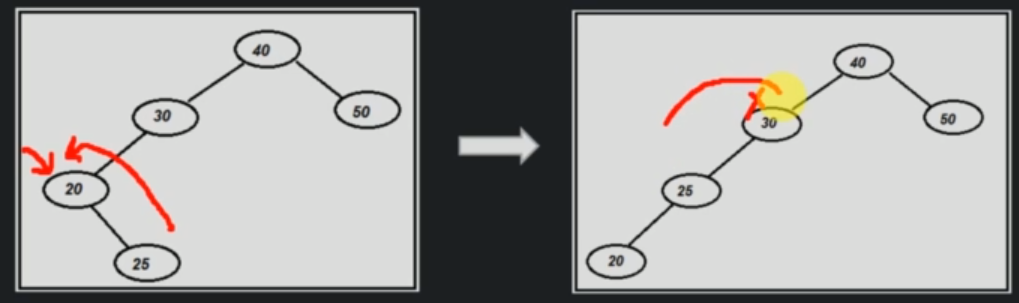
Then we can do a right rotation.
leftRotate(currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild)
newRoot = currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild.right
currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild.right = currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild.right.left
newRoot.left = currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild
currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild.height = calculateHeight(currentDisbalancedNodesLeftChild)
newRoot.height = calculateHeight(newRoot)
return newRoot
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
3. Right Right contidition (RR)¶
It is exactly opposite of the LL condition. We apply leftRotate, but on the disbalancedNode instead of it's left child like in the LR condifition.
leftRotate(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot = currentDisbalancedNode.right
currentDisbalancedNode.right = currentDisbalancedNode.right.left
newRoot.left = currrentDisbalancedNode
CurrentDisbalancedNode.height = calculateHeight(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot.height = calculateHeight(newRoot)
return newRoot
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
4. Right Left condition (RL)¶
We do a right rotation on disbalanced node's child. Then left rotation on the disbalanced node.
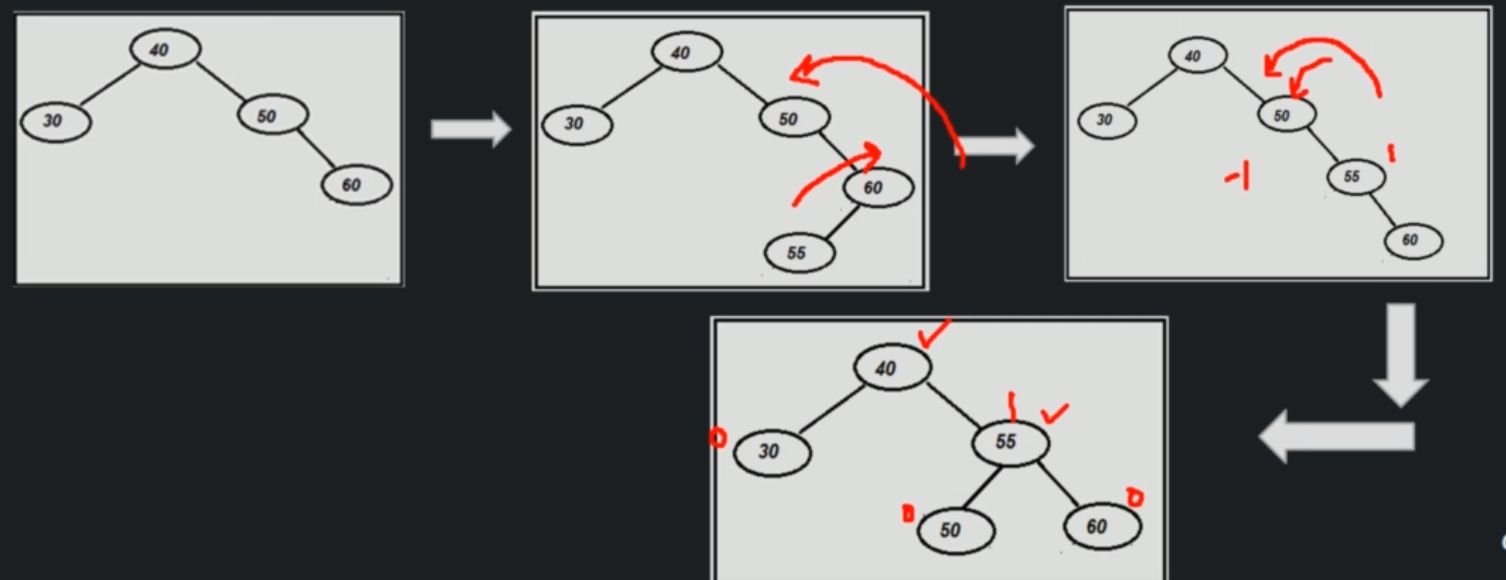
rightRotate(currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild)
newRoot = currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild.left
currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild = currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild.left.right
newRoot.right = currentDisbalancednodesRightChild
currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild.height = calculateHeight(currentDisbalancedNodesRightChild)
newRoot.height = calculateHeight(newRoot)
return newRoot
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
leftRotate(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot = currentDisbalancedNode.right
currentDisbalancedNode.right = currentDisbalancedNode.right.left
newRoot.left = currrentDisbalancedNode
CurrentDisbalancedNode.height = calculateHeight(currentDisbalancedNode)
newRoot.height = calculateHeight(newRoot)
return newRoot
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
Insert, end-to-end case¶
We are going to construct an example where all of the previously mentioned cases will be called.
Node insert( Node root, int data )
if(root == null) return new Node(data) // BST condition
else if (data <= root.data ) root.left = insert(root.left, data) // BST condition
else root.right = insert(root.right, data) // BST condition
int balance = height(root.left) - height(root.right)
if(balance > 1) // if left subree is overloaded
if( height root.left.left >= height(root.left.right) )
RightRotation(root) // LL condition
else // LR condition
LeftRotation(root.left)
RightRotation(root)
else if (balance < -1) // if right subtree is overloaded
if height(root.right.right) >= height(root.right.left)
LeftRotation(root) // PR condition
else // RL condition
return RightRotation(root.right)
LeftRotation(root)
root.height = max(root.left, root.right) + 1
return root
Time complexity - O(log n)
Space complexity - O(log n)
Deletion of a node¶
There can be 3 cases: 1. Tree does not exist 2. Rotation is not required (BST conditions) 3. Rotation is required
deleteNode(currentNode, valueToBeDeleted):
if(currentNode === null) return null
if(valueToBeDeleted < currentNode.value)
currentNode.left = deleteNode(currentNode.left, valueToBeDeleted)
else if (valueToBeDeleted > currentNode.value)
currentNode.right = deleteNode(currentNode.right, valueToBeDeleted)
else
if current node have both children then find minimum element from right subtree (case 3)
retplace current node with minimum node from right subree and delete minimum node from right
else if nodeToBeDeleted has only left child (case 2)
currentNode = currentNode.left
else if nodeToBeDeleted has only right child (case 2)
currentNode = currentNode.right
else // if nodeToBeDeleted do not have any children (case 1)
currentNode = null
int balance = checkBalance(currentNode.left, currentNode.right)
if(balance > 1)
if(checkBalance(currentNode.left.left, currentNode.left.right) > 0)
currentNode = rightRotate(currentNode) // LL condition
else
currentNode.left = leftRotate(currentNode.left) // LR
currentNode = rightRotate(currentNode)
else if balance < -1
if(checkBalance(currentNode.right.right, currentNode.right.left) > 0)
currentNode = leftRotate(currentNode) // RR
else
currentNode.right = rightRotate(currentNode.right) // RL
currentNode = leftRotate(currentNode)
if(currentNode.left !== null)
currentNode.left.setHeight(calculateHeight(currentNode.left)
if(currentNode.right !== null)
currentNode.right.setHeight(calculateHeight(currentNode.right)
currentNode.setHeight(calculateHeight(currentNode));
return currentNode
Time complexity - O(log n)
Space complexity - O(log n)
Deletion of entire AVL tree¶
delete()
root = null
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
When we set the root to null, automatically it's children are orphaned and garbage collector deletes the entire tree.
Time & Space complexity in AVL tree¶
| Time complexity | Space complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| create tree | O(1) | O(1) |
| insert value | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| delete value | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| search | O(log n) | O(log n) |
| traverse | O(n) | O(n) |
| delete tree | O(1) | O(1) |