What is a tree¶
A tree is a data structure that is used to represent data in a hierarchical form. Every node has 2 components - data that it holds and reference to it's parent.
At the very top it has a root node with a left sub-category and right sub-category under it.
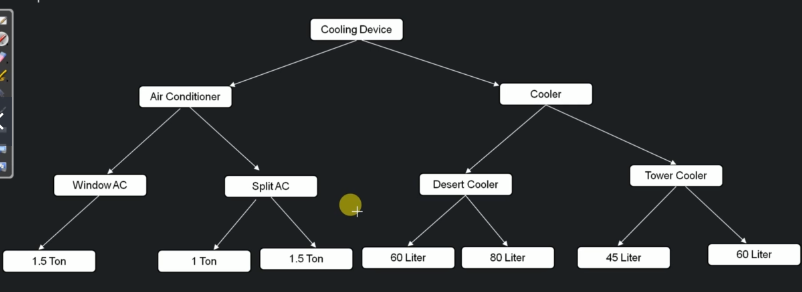
Tree terminology¶
- Root - node with no parent
- Edge - link from parent to child
- Leaf - node with no children
- Sibling - children of the same parent
- Ancestor - parent, it's parents ... of a given node
- Depth - length of the path from root to node
- Height - Length of the path from node to the deepest node
- Predecessor - Immediate previous node inorder traversal of the binary tree
- Successor - immediate next node inorder traversal of the binary tree
Predecessor example:
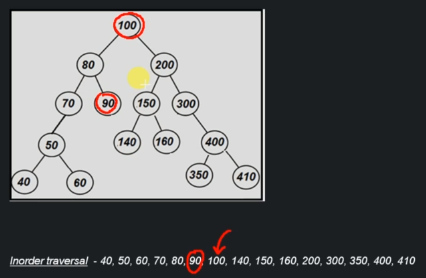
Starts with the left subtree, then root node, then right subtree.
What is a binary tree¶
- A tree is called a binary tree if each node has zero, one or two child nodes.
- It is a family of data structure (BST, Heap tree, AVL, Red-Black, Syntax tree, Huffman cofing tree etc.)
Used to solve specific problems like: - Huffman coding - Heap (priority queue) - Expression parsing
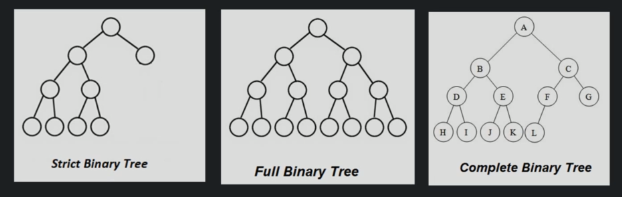
Types of binary trees¶
- Strict binary tree - if each node has either 2 children or none
- Full binary tree - if each non leaf node has 2 children and all leaf nodes are at same level
- Complete binary tree - if all levels are completely filled except possibly the last level and the last level has all keys as left as possible.
Common operations¶
- Creating a tree
- Inserting a node
- Deleting a node
- Searching for a value
- Traversal of all nodes
- Deletion of the tree