Circular single linked list¶
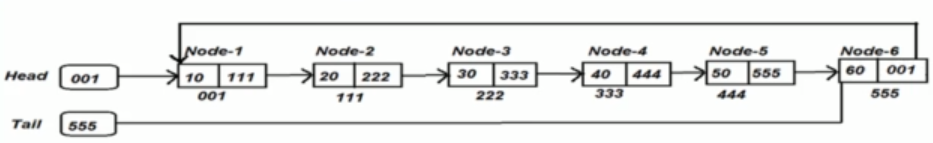
The same principes as the Single Linked List applies to the Circular Single Linked List. The only difference is that the last element points to the first one.
Creating¶
When we want to create a circular single linked list, it consists of a few steps:
- We create a blank head reference
- We create a blank tail reference
- We initialize them both with null
- We create a blank node
- We initialize it with reference to the first node (self)
- We initialize the data part of it
- We update the head reference to the node
- We update the tail reference to the node
createSingleLinkedList(nodeValue):
create a blank node
node.value = nodeValue
node.next = node
head = node
tail = node
createSingleLinkedList(nodeValue):
create a blank node -------------- O(1)
node.value = nodeValue ----------- O(1)
node.next = node ----------------- O(1)
head = node ---------------------- O(1)
tail = node ---------------------- O(1)
Time complexity O(1)
Space complexity O(1)
Inserting data in Circular Single Linked List¶
When we want to insert a new node, we can have 3 scenarios: - Inserting at the start of linked list
We have to create a new node, hold a reference to the first element and update the head to reference it.
-
Inserting at the end of linked list
We have to create a new node, update the previous element as well as the tail to point to it, reference self to the first element.
-
Inserting at a specified location in linked list
We have to create a new node, update the previous element to point to it, hold the reference to the next element.
insertLinkedList(head, nodeValue, location):
create a blank node
node.value = nodeValue
if (!existsLinkedList(head))
return error // Linked List does not exist
else if (location equals 0) // insert at first position
node.next = head
head = node; tail.next = head
else if (location equals last) // insert at last position
node.next = head
tail.next = node
tail = node // to keep track of last node
else
loop: tmpNode = 0 to location - 1
node.next = tmpNode.next
tmpNode.next = node
Traversing in Circular Single Linked Lists¶
TraverseLinkedList(head):
if head == NULL
return;
loop: head to tail
print curentNode.value
TraverseLinkedList(head):
if head == NULL ---------------- O(1)
return; -------------------- O(1)
loop: head to tail ------------- O(n)
print curentNode.value -- O(1)
Time complexity O(n)
Space complexity O(1)
Searching a node in Circular Single Linked List¶

SearchNode(head, nodeValue):
loop: tmpNode = start to tail
if (tmpNode.value == nodeValue)
print tmpNode.value
return true
return false
SearchNode(head, nodeValue):
loop: tmpNode = start to tail --------------- O(n) |
if (tmpNode.value == nodeValue) -- O(1)| |- O(n)
print tmpNode.value ---------- O(1)|- O(1) |
return true ------------------ O(1)|
return false ---------------------------------------- O(1)
Time complexity - O(n)
Space complexity - O(1)
Delete a node from a Circular Single Linked List¶

There can be 3 cases: - Delete first node - Delete last node - Delete any other node
deleteNode(head, Location):
if( !existsLinkedList(head))
return error // Linked List does not exist
else if (location == 0) // delete first element
head = head.next;
tail.next = head;
if (this was the only element in the list):
head = tail = node.next = null
else if (location >= last)
if( current node is only node in list ):
head = tail = node.next = null; return;
loop until 2nd last node (tmpNode)
tail = tmpNode;
tmpNode.next = head;
else // if any internal node needs to be deleted
loop: tmpNode = start to location -1
tmpNode.next = tmpNode.next.next
deleteNode(head, Location):
if( !existsLinkedList(head)) -------------------------- O(1)
return error // Linked List does not exist -------- O(1)
else if (location == 0) // delete first element ------- O(1)
head = head.next; -------------------------------- O(1)
tail.next = head; --------------------------------- O(1)
if (this was the only element in the list): ------- O(1)
head = tail = node.next = null ---------------- O(1)
else if (location >= last) ---------------------------- O(1)
if( current node is only node in list ): ---------- O(1)
head = tail = node.next = null; return; ------- O(1)
loop until 2nd last node (tmpNode) ---------------- O(n)
tail = tmpNode; ------------------------------ O(1)
tmpNode.next = head; -------------------------- O(1)
else // if any internal node needs to be deleted ------ O(1)
loop: tmpNode = start to location -1 -------------- O(n)
tmpNode.next = tmpNode.next.next ------------------ O(1)
Time Complexity - O(n)
Space Complexity - O(1)
Deletion of entire cicular single linked list¶

DeleteLinkedList(head, tail):
head = null
tail.next = null
last = null
DeleteLinkedList(head, tail): ----- O(1)
head = null ------------------- O(1)
tail.next = null -------------- O(1)
last = null ------------------- O(1)
Time complexity - O(1)
Space complexity - O(1)
Time & Space complexity of Circular Single Linked List¶

| Time complexity | Space complexity | |
|---|---|---|
| Creating | O(1) | O(1) |
| Insertion | O(n) | O(1) |
| Searching | O(n) | O(1) |
| Traversing | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deletion | O(n) | O(1) |
| Deleting whole list | O(1) | O(1) |